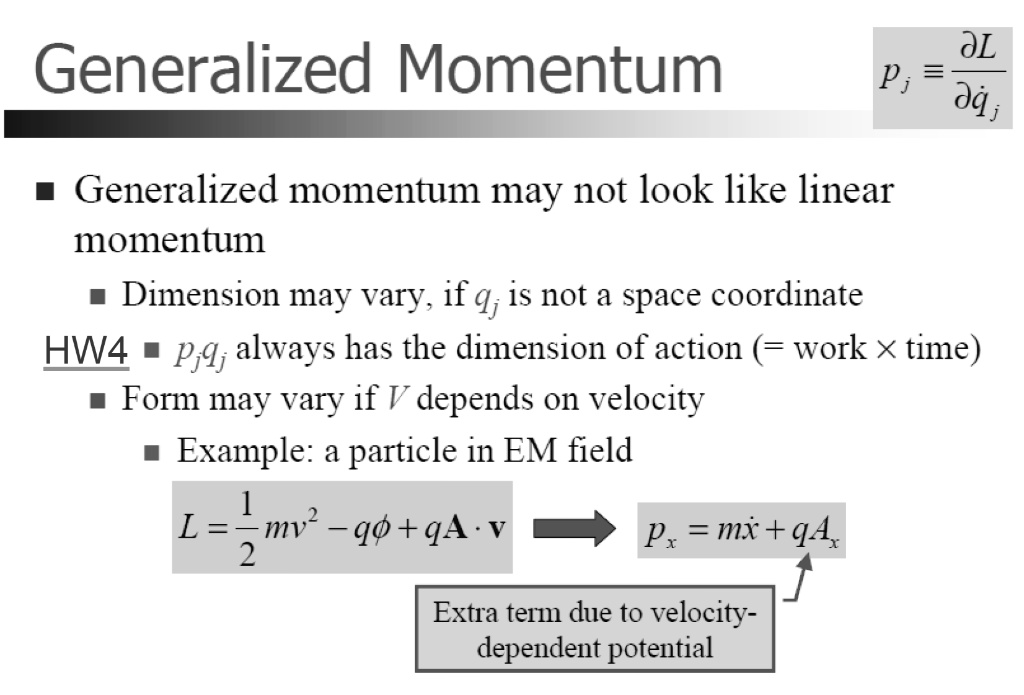
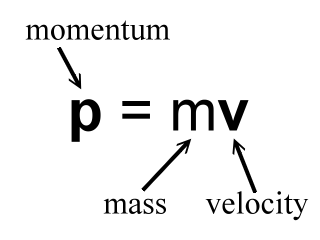
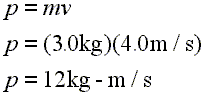Momentum p = m v Momentum = mass * velocity momentum is directly proportional to an object's mass momentum is directly proportional to the object's velocity. - ppt download

If momentum P, area A and time T are taken to be fundamental quantities, then the energy has the dimensional formula
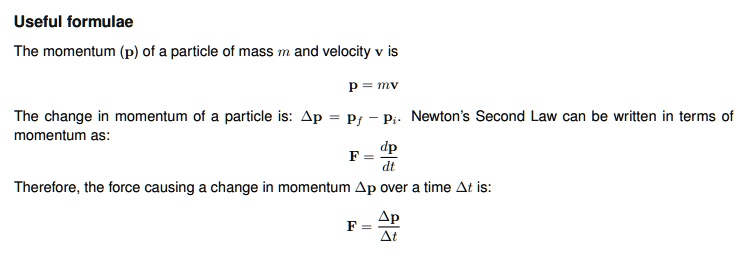
SOLVED: Useful formulae The momentum (p) of particle of mass mn and velocity p = MnV The change in momentum of a particle is: Ap = Pf Pi. Newtons Second Law can

The linear momentum P of a body varies with time and is given by the equation P=x+yt2, where x and y - YouTube

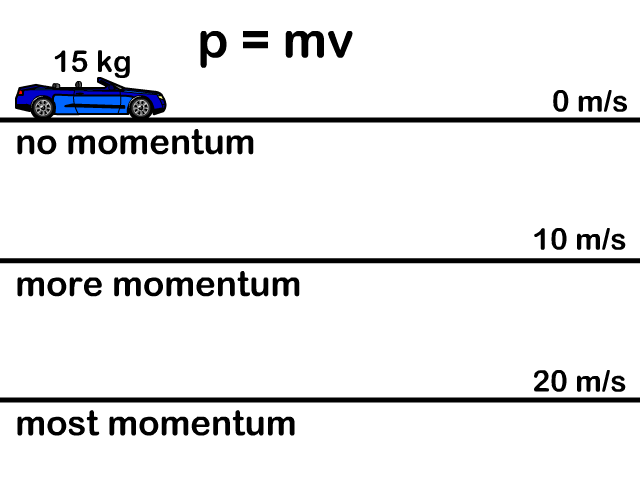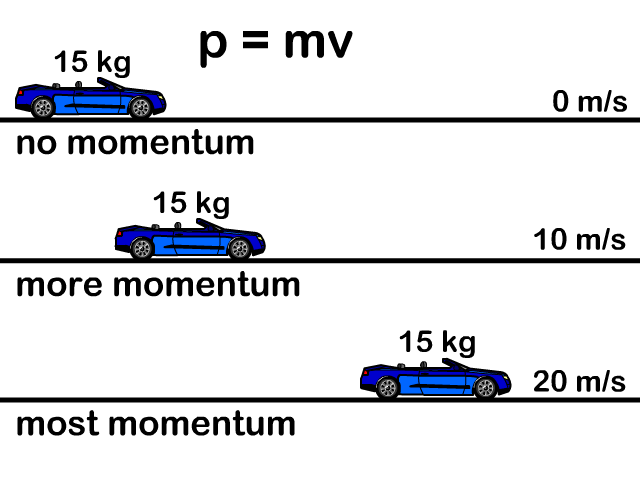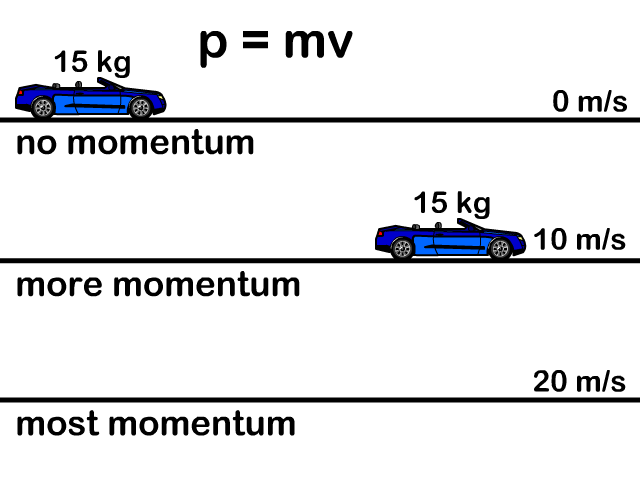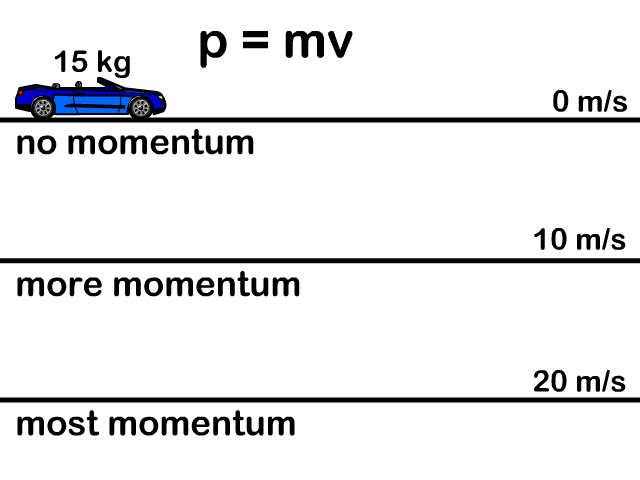
Momentum Momentum is Momentum = P = Units = Momentum is a vector quantity – it has ______ and ______ SO: the bigger the object, - ppt download

A particle. has the position vector r = vec i - 2vec j + k and the linear momentum p = 2vec i - vec j + vec k . Its angular momentum about the origin is

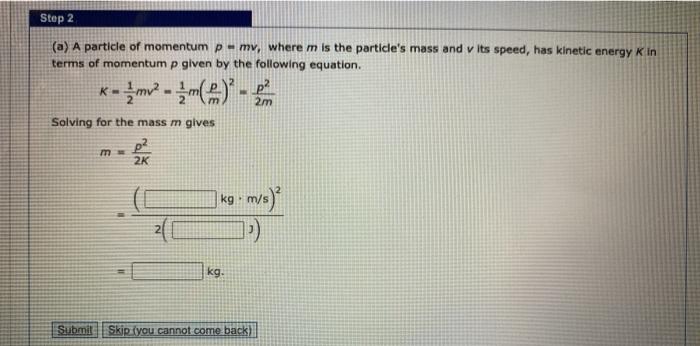
A particle of mass m, kinetic energy K and momentum p collision head on elastically with another - YouTube

ENERGY AND POWER THERMODYNAMICS. MOMENTUM MOMENTUM P = mv FORCE F = ma = mv/t IMPULSE Ft = mv = P (Momentum) MOMENTUM IS ALWAYS CONSERVED There has been. - ppt download
23.A body is projected at angle 30 degree with the horizontal with momentum p. At its highest point the magnitude of momentum is

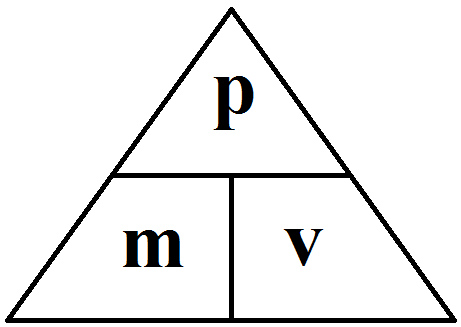
MOMENTUM. DEFINITIONS Linear momentum (p) is defined as the product of mass (m) and velocity (v): p = m x v SI-unit of momentum is 1 kg ∙ m ∙ s -1, alternative. - ppt download
The momentum p (in kg m/s) of a particle is varying with time t ( in s) as p= 2+3t square. The force acting on the particle at t= 3 s will